Top 10 Reagent Chemicals You Should Know About?
In the world of chemistry, knowledge of reagent chemicals is essential. These substances play a crucial role in various experiments and industrial processes. Understanding their properties can lead to better results and innovations in research. Each reagent chemical serves a specific function, from catalysts to indicators.
It's easy to overlook the importance of these chemicals. Many students and professionals might not fully grasp their potential. Using the wrong reagent can lead to unexpected outcomes. Familiarity with top reagent chemicals is vital for success.
This article aims to provide insight into the ten most significant reagent chemicals. Each selection is based on common use and impact in laboratories. We will explore their roles, benefits, and some potential misconceptions. Being informed will help you navigate the intricate world of chemistry more effectively.
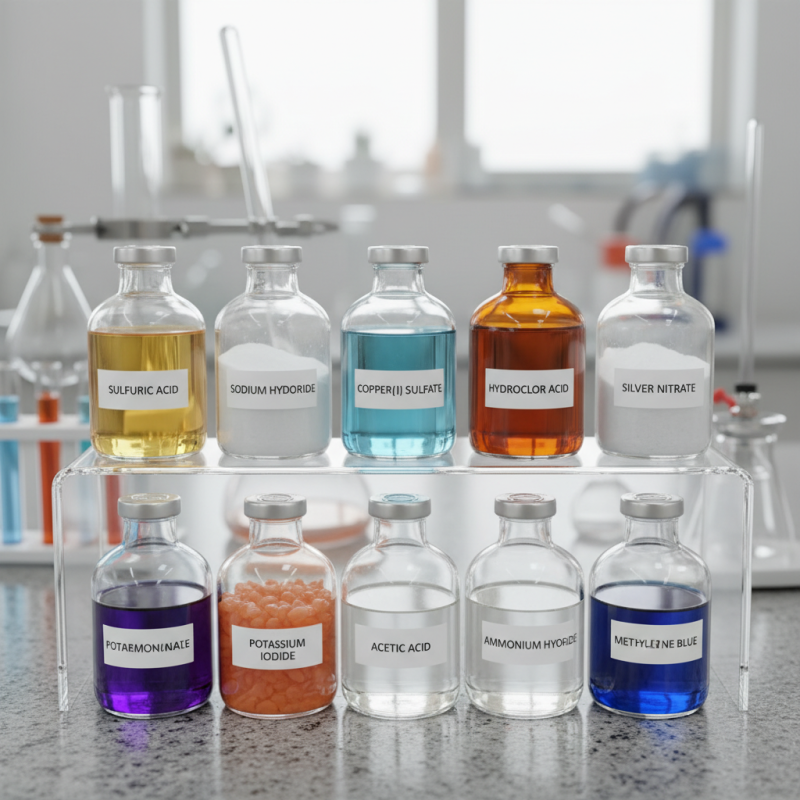

Overview of Reagent Chemicals and Their Importance
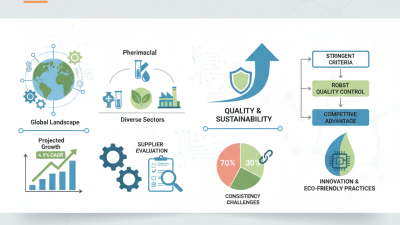
Reagent chemicals play a crucial role in various industries, especially in scientific research and chemical manufacturing. They serve as essential substances used to create chemical reactions or detect the presence of other compounds. According to a recent report by the Global Chemicals Outlook, the reagent chemicals market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.5% over the next five years. This growth underscores their significance in both education and industry.
Understanding the fundamentals of reagent chemicals is vital. These substances come in various forms, including solids, liquids, and gases. They have diverse applications, from analytical testing to synthesizing new materials. Laboratory technicians often rely on them for precise measurements. Many universities emphasize the importance of hands-on experience with these reagents. Students who engage in laboratory work become adept at handling and understanding the properties of these chemicals.
Tips: Always read safety data sheets before using any reagents. This practice enhances lab safety and minimizes risks. Additionally, consider proper storage conditions. Reagents must be stored in designated environments to maintain their stability. Failure to do so can lead to inaccurate results in experiments, highlighting the need for meticulous laboratory practices.
Common Applications of Reagent Chemicals in Research

Reagent chemicals play a crucial role in various research fields. They serve as essential tools in laboratories for experimentation. These chemicals help scientists identify components, reactions, and properties of materials. One notable application is in analytical chemistry. Here, reagents aid in qualitative and quantitative analysis. They help determine the concentration and presence of specific substances.
Another important area is biochemistry. Reagent chemicals are vital for enzyme assays and protein studies. They can reveal interactions between molecules. Understanding these interactions is crucial for drug discovery. Nevertheless, researchers sometimes misuse reagents. A lack of precision can lead to inaccurate results. It's important to approach experiments with care. Every reagent has its own set of properties and potential hazards. Ignoring safety guidelines can result in unintended reactions.
In environmental science, reagent chemicals help monitor pollutants. For instance, testing water quality often requires specific reagents. They can indicate the presence of heavy metals or toxins. This application is vital for public health and safety. However, the impact of these chemicals on the environment needs consideration. Researchers must keep this in mind. Balancing scientific exploration with responsible usage remains a challenge.
Top 10 Essential Reagent Chemicals for Laboratories
When it comes to laboratory work, certain reagent chemicals stand out as essential.
Water, as a solvent, is fundamental. It is used in countless reactions and dilutions. Over 90% of laboratory protocols mention water as a key component.
Its purity directly affects the outcome of experiments. Therefore, ensuring high-quality distilled or deionized water is crucial.
Sodium chloride is another critical reagent. Commonly used in buffer solutions, it helps maintain osmotic balance in biological experiments.
Studies show that 75% of life science protocols involve sodium chloride in some form.
Its versatility makes it indispensable, but improper concentrations can lead to skewed results. Many labs often overlook the importance of accurate measurements.
Acids such as hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid also play pivotal roles in numerous reactions. They are used for titrations, pH adjustments, and as catalysts.
Nevertheless, handling these acids comes with risks. Incorrect usage can lead to dangerous situations. Toxic fumes and corrosive burns are potential hazards that require constant vigilance.
Labs should provide ample training to workers to mitigate these risks.
Safety and Handling Practices for Reagent Chemicals
Handling reagent chemicals requires careful attention to safety. Always review the safety data sheet (SDS) before starting any experiment. This document provides essential information about the substances, their hazards, and safe handling practices. Make it a habit to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats. Each chemical has its own risk profile. Ignoring this can lead to accidents.
Ventilation is crucial when working with volatile chemicals. Be aware of fume hoods and ensure they are functioning properly. A poorly ventilated area can quickly become hazardous. If you notice a strong odor, stop working immediately. Familiarize yourself with emergency procedures. Knowing how to respond can mitigate serious incidents.
Accidental spills can happen, no matter how careful you are. Develop a spill response plan and practice it regularly. This includes knowing where absorbents are stored and how to dispose of them safely. Regularly check the condition of containers and labels. Damaged packaging can lead to leaks and contamination. It’s essential to report any issues to supervisors promptly. Always stay vigilant and question your practices. Continuous reflection will improve safety over time.
Top 10 Reagent Chemicals You Should Know About
Future Trends in Reagent Chemical Development and Usage
The future of reagent chemical development is vibrant yet complex. Emerging trends indicate a shift towards sustainable practices. Researchers are prioritizing eco-friendly chemicals. This is a crucial response to global environmental challenges. Innovations in biodegradable reagents are increasing. They minimize ecological footprints and enhance safety. Many scientists are adopting green chemistry principles in their work.
Additionally, automation and artificial intelligence are playing significant roles. High-throughput screening enables rapid testing of new reagents. These innovations can streamline processes but introduce challenges. There is a constant need for adaptation. New technologies often outpace regulatory frameworks, creating uncertainty. Researchers must remain vigilant about safety and compliance issues. Moreover, collaborations across disciplines are becoming more common. This cross-pollination of ideas can spark groundbreaking developments but sometimes leads to conflicting priorities.
As the landscape evolves, there's a risk of overlooking traditional methodologies. While innovation is essential, the importance of foundational knowledge should not be diminished. Balancing the old with the new requires careful consideration. This tension highlights the need for ongoing education and reflection in the field. The path forward in reagent chemistry is promising, yet fraught with challenges.
Top 10 Reagent Chemicals You Should Know About
| Reagent Chemical | Common Uses | Safety Hazards | Future Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium Chloride | Food preservation, chemical synthesis | May cause hypernatremia | Increased use in biochemistry |
| Acetic Acid | Food additive, solvent, reagent | Corrosive, flammable | Green chemistry applications |
| Hydrochloric Acid | pH adjustment, cleaning agent | Corrosive, toxic fumes | More efficient industrial processes |
| Sulfuric Acid | Battery acid, fertilizer production | Highly corrosive, toxic | Innovations in recycling |
| Ethanol | Solvent, fuel, antiseptic | Flammable, intoxicant | Biofuel developments |
| Ammonium Hydroxide | Cleaning agent, fertilizer | Caustic, irritant | Sustainable agricultural practices |
| Potassium Permanganate | Water treatment, disinfection | Oxidizer, harmful if ingested | Advanced oxidation processes |
| Sodium Bicarbonate | Baking, pH balancer | Generally safe, irritation possible | Increased dietary uses |
| Calcium Carbonate | Pharmaceuticals, antacids | Inhalation hazard | Emerging nanotechnology applications |
| Silver Nitrate | Photography, antiseptic | Toxic, stains skin | Advances in medical applications |
Related Posts
-
How to Source Quality Chemical Raw Materials for Your Business Needs
-

Top 10 Essential Chemicals in Chemistry You Need to Know
-

Why Are Chemical Raw Materials Essential for Modern Manufacturing Processes?
-

How to Choose the Right Chemical Vendors for Your Business Needs in 2025
-

What is Industrial Chemistry and Why is it Important?
-

Top 10 Reagent Chemicals You Need for Your Laboratory Experiments
Contact Us
We offer a just-in-time delivery solution supplying the highest quality materials to our customers. Get in touch today and learn how we can help your company.
Get in touch